中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (27): 4318-4323.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.27.010
• 细胞与组织移植 cell and tissue transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
体表脉冲电刺激对昆明小鼠心电活动的影响
李永林1,张 辉1,史若飞2,汤小曼1,解 力1,黄 吕1,张晓刚1
- 1重庆医科大学附属第一医院心内科,重庆市 400042;2重庆市第四人民医院,重庆市 400014
Effect of surface electric-impulse stimulation on cardiac electrical activity of Kunming mice
Li Yong-lin1, Zhang Hui1, Shi Ruo-fei2, Tang Xiao-man1, Xie Li1, Huang Lv1, Zhang Xiao-gang1
- 1 Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400042, China; 2 Chongqing Fourth People’s Hospital, Chongqing 400014, China
摘要:
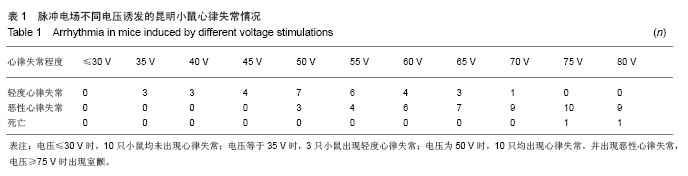
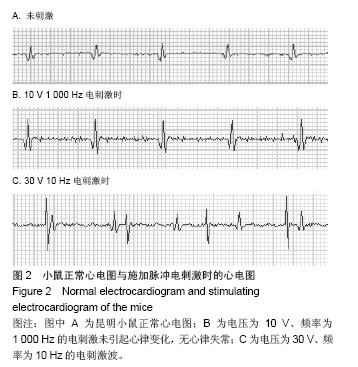
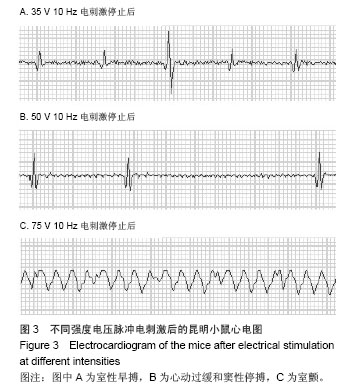
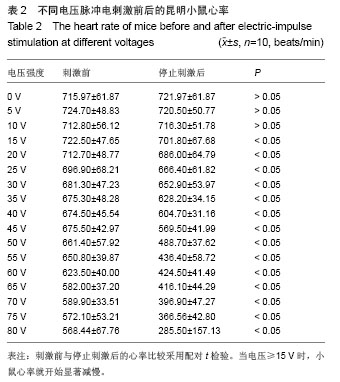
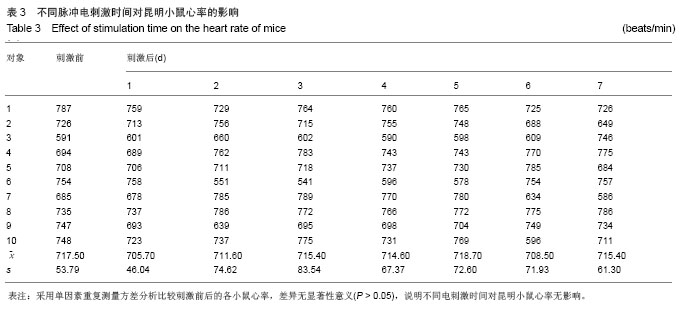
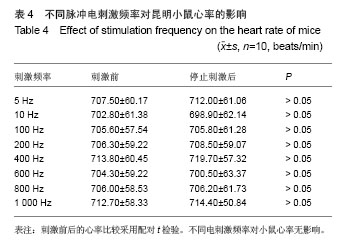
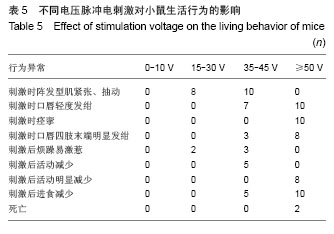
背景:使用不同强度、频率及时间的电刺激作用于人体,可能产生各种不同的病理生理反应。 目的:观察体表脉冲电刺激对小鼠心律及心率的影响。 方法:将30只昆明小鼠随机分为3组,每组10只,用BL-420F型生物机能实验系统提供刺激电源,对3组昆明小鼠分别予以不同电压、不同时间、不同频率的体表电刺激,然后观察Ⅱ导联心电图、小鼠得全身反应与局部变化。 结果与结论: ≤10 V的电刺激对小鼠心率无明显影响,并且未出现心律失常;电压≥15 V时,电刺激可使小鼠心率减慢,停止30 min后心率恢复正常;电压≥35 V时,小鼠出现心率减慢和心律失常,并且停止刺激后心率不能恢复正常;电压>75 V后,小鼠出现室颤。电压为10 V时,脉冲电刺激时间和频率变化对小鼠心电活动影响不显著。说明脉冲电刺激对小鼠心电活动的影响主要由所用电压高低不同引起,电压≤10 V时对小鼠心电活动无影响;脉冲电刺激时间与电场频率对小鼠心电活动影响不明显。
中图分类号:

.jpg)